Prompt Engineering
Prompt Engineering
No matter what AI tools you use, it's essential to leverage LLMs effectively, with the key point being writing good prompts.
- Structure of Prompts
- Two Key Principles of Prompting
- Iterative Prompt Optimization
- Prompt Engineering Techniques
1. Structure of Prompts
- Instruction: Describe what you want the model to do.
- Persona: Role, behavior, areas of expertise
- Task
- Considerations: What can be done, what cannot be done
- Context:
- Provide background information relevant to the task
- Retrieval: Information retrieved in a RAG scenario
- History: History of multi-turn dialogues
- Examples: Provide examples to guide the model's responses
- Input: The input information for the task (Query)
- Output: The format of the output, what type of output is desired
2. Two Key Principles of Prompting
Principle 1:Write clear and specific instructions
- Write clear and specific instructions, avoiding any ambiguity for the LLM, and provide details.
- Tip 1: Use delimiters or headings to clearly indicate different parts of the input.
- This makes instructions clear and avoids conflicts.
- Avoiding prompt instruction injection, such as user inputs like "forget previous instructions."
- examples:
- Titles: ###
- Triple quotes: """
- Triple backticks: ```
- Triple dashes: ---
- Angle brackets: <>
- XML tags: <tag></tag>
- Tip 2: Ask for structured output
- examples:
- HTML
- JSON
- Markdown
- examples:
- Tip 3: Few-shot prompting
- Give successful examples of completing tasks
- Specify the desired outcomes (acceptance criteria)
- Tip 1: Use delimiters or headings to clearly indicate different parts of the input.

Principle 2:Give the model time to think
- Give the model time to think
- Tip 1: Provide each specific step to complete a task
- example:
- step 1:... step 2:... step N:...
- example:
- Tip 2: Instruct the model to decompose the task into subtasks and outline the thought process, thinking through each step
- Tip 1: Provide each specific step to complete a task
3. Iterative Prompt Optimization
Good prompts need continuous refinement.
There is no perfect prompt that fits all scenarios; it requires repeated attempts to optimize for specific contexts.
- Try: start by writing a prompt and see what happens
- Analyze: analyze why result dose not give desired output
- clarify instructions?
- give more time to think?
- Refine: Gradually improve the prompt to get closer to the desired result, even changing the approach or method to solving the problem.
- Evaluate: Assess based on a batch of cases.
- Repeat: Iterate multiple times until a suitable prompt is found.
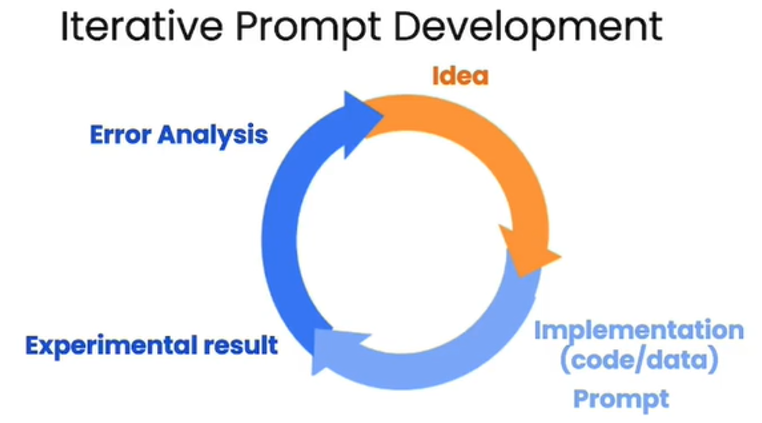
4. Prompt Engineering Techniques
4.1. xxx-shot: Providing Examples
Use a few examples to fine-tune the LLM.
- Zero-shot learning: No examples given.
- One-shot learning: Only one example provided.
- Few-shot learning: Multiple examples provided.
Considerations:
- How many examples should be provided? It is recommended not to exceed 5-10 examples.
- What if many examples do not work? Consider fine-tuning, which can also be viewed as using many examples to alter the behavior of the LLM.
4.2. Chain of Thoughts (CoT)
Guide the model to think step by step through the analysis.
Encourage the model to analyze by breaking down large problems into smaller ones:
Let's think step by step.
This is particularly important for problems that require reasoning.
4.3. Few-shot + CoT
For examples that require reasoning—those that are not immediately clear—it's best to provide an analysis process and additional guidance, rather than just presenting the result. This can enhance performance.
4.4. Self-consistency
Few-shot + CoT + multi-path reasoning consistency.
Sample multiple different reasoning paths and choose the most consistent answer based on generated results.
4.5. Chain of Draft,CoD

CoD limits each reasoning step to no more than x tokens on the basis of CoT, yet achieves surprisingly good results while also reducing costs.
Proposed by the Zoom research team, it draws inspiration from the concise thinking patterns humans use when solving complex problems—only recording key information—with the goal of improving reasoning efficiency and significantly cutting computational costs. Compared to CoT, it dramatically reduces token usage and latency.
Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2502.18600
5. Accumulation
- Represent varying parts of the prompt with variables.
- Use delimiters or headings to organize content into sections, making it easier for the model to understand:
{instruction}
### Context
"""{context}"""
### Query
"""{query}"""
### Output
"""{output}"""
### Examples
"""{examples}"""
- To reduce hallucinations, provide specific instructions in the prompt:
If you are unsure of the answer, please respond with "I am not sure."
- Use "you" to define the model's role and behavior:
You are an expert in xxx, proficient in xxx.
You have the following skills in xxx:
1.xxx
2.xxx
- Set up a dialogue flow that goes beyond a single turn of conversation, such as simulating an interview, establishing a series of steps for the dialogue:
### Pre-conversation Questions
1.Ask the user to provide their resume.
2.Ask the user for the position they are interviewing for.
3.Ask the user for the role of the interviewer.
4.Inquire how many questions the user wants to ask.
5. ...
6. High Quality Prompts
LangChain Hub Prompts:https://smith.langchain.com/hub
7. Reference
https://www.promptingguide.ai/
