Agent & MultiAgent
Agent & MultiAgent
- Agent
- MultiAgent
- ReAct
1. Agent
Agent = LLM + Observation + Thinking + Action + Memory
- LLM: Processes information, makes decisions, and executes actions
- Observation: Perception of the environment. An agent can receive messages from other intelligent entities in the environment.
- Thinking: Analyzes the results of observations and memory content, considers what action to take next. This decision-making ability is provided by the LLM.
- Action: The result of observation and thinking, determining what specific tasks to carry out. This is similar to tools in LangChain.
- Memory: Stores past experiences.
Difference Between Agent and Chain
Similarities:
- Both complete a series of tasks step by step to ultimately achieve complex goals.
Differences:
- Chain: A predefined sequence of tasks, i.e., static (what should be done in each step is determined in advance).
- Agent: The tasks in each step are not predefined and can vary depending on the user's questions or scenarios (dynamic).
2. ReAct
Paper Name: ReAct : SYNERGIZING REASONING AND ACTING IN LANGUAGE MODELS
Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2210.03629
Github: https://github.com/ysymyth/ReAct

3. AutoGPT
Github: https://github.com/Significant-Gravitas/AutoGPT
Paper Name: Auto-GPT for Online Decision Making: Benchmarks and Additional Opinions
Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.02224
An autonomous agent only needs to be told the requirements, and does not need guidance on what to do first or next. It can autonomously propose a plan, execute it, and complete the task.
4. MetaGPT
Github: https://github.com/geekan/MetaGPT
Paper Name: METAGPT: META PROGRAMMING FOR A MULTI-AGENT COLLABORATIVE FRAMEWORK
Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2308.00352
5. HuggingGPT
Paper Name: HuggingGPT: Solving AI Tasks with ChatGPT and its Friends in Hugging Face
Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2303.17580
Github: https://github.com/microsoft/JARVIS
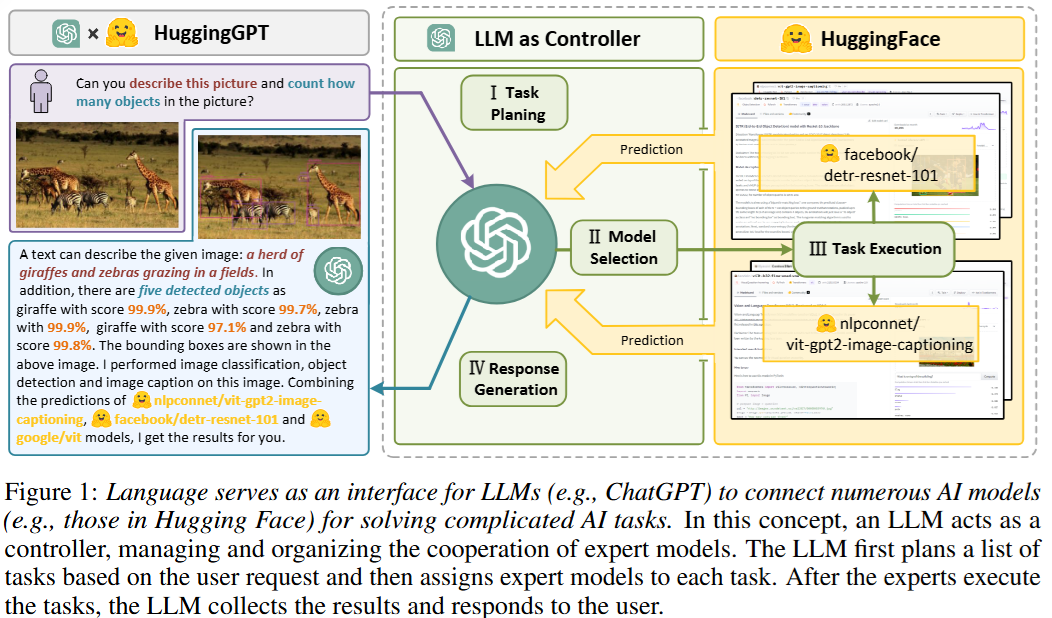
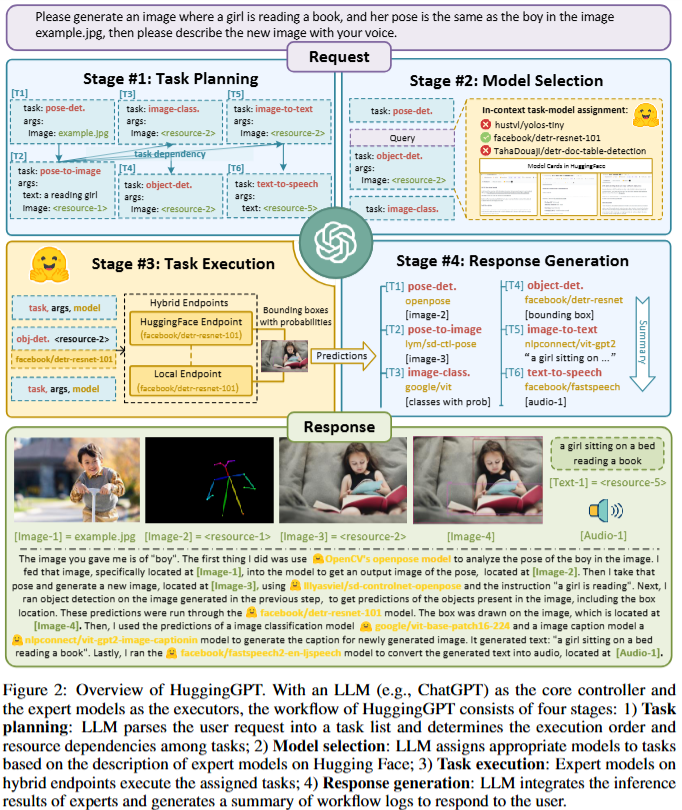
Four Stages
- Task Planning
- Model Selection (from Hugging Face)
- Task Execution
- Response Generation
6. generative_agents: Stanford Town
Paper Name: Generative Agents: Interactive Simulacra of Human Behavior
Paper: https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3586183.3606763
Github: https://github.com/joonspk-research/generative_agents
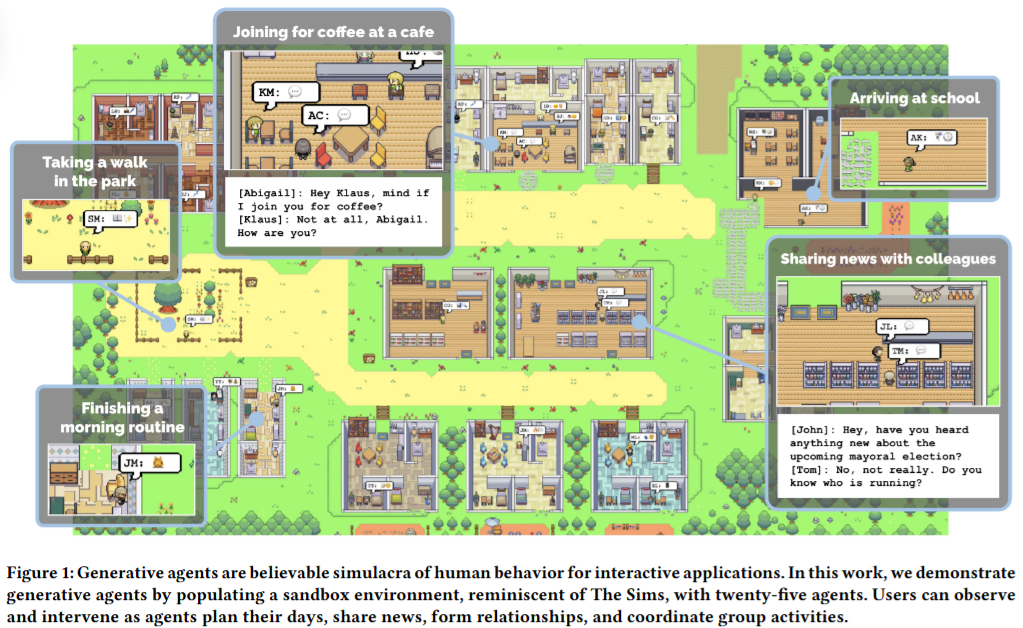
This is one of the most influential works in this field, providing an effective foundation for future multi-agent collaboration.
There are many potential application scenarios to explore in the realm of generative multi-agents.
6.1. Design of Each Agent's Properties
- Basic Information
- Past Experiences
- Interests and Hobbies
6.2. Memory Design
Recency (Time proximity):
- The closer an event is to the present, the more weight it carries.
Importance:
- Some events are more important than others, e.g., "Waking up" < "Promotion".
Relevance
- Cosine Similarity
score = Recency x + Importance x + Relevance x
Reflection Extraction: Summarizing the Memory Stream
- Scheduled Task: Summarize periodically after a certain time.
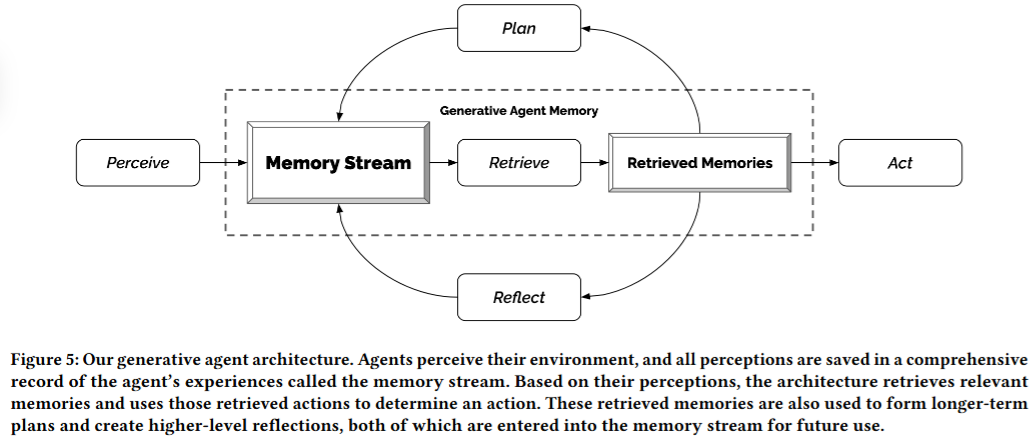
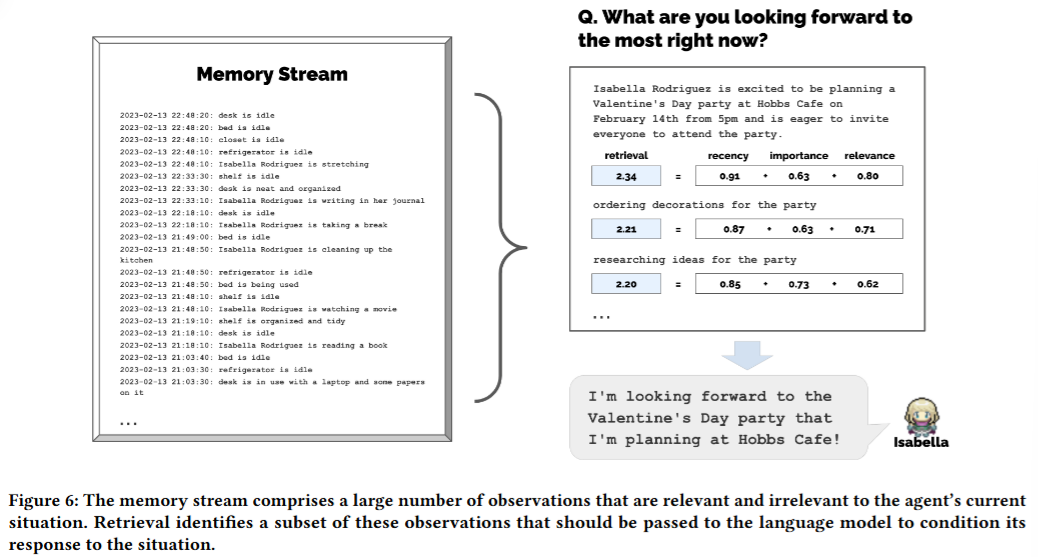
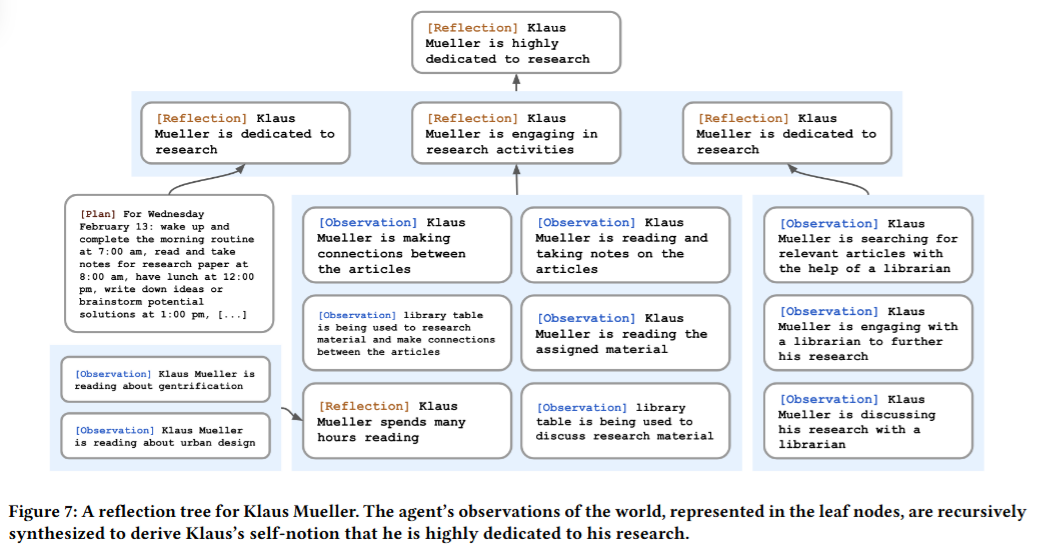
6.3. Planning: Generating a Daily Plan for Each Agent
- Daily routine
- Add unique schedules based on the characteristics of the agent
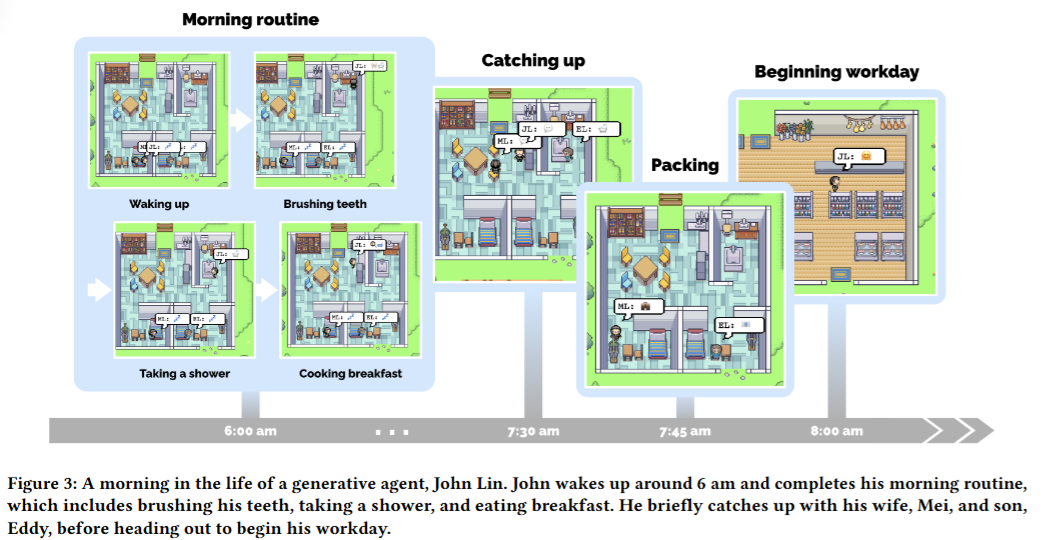
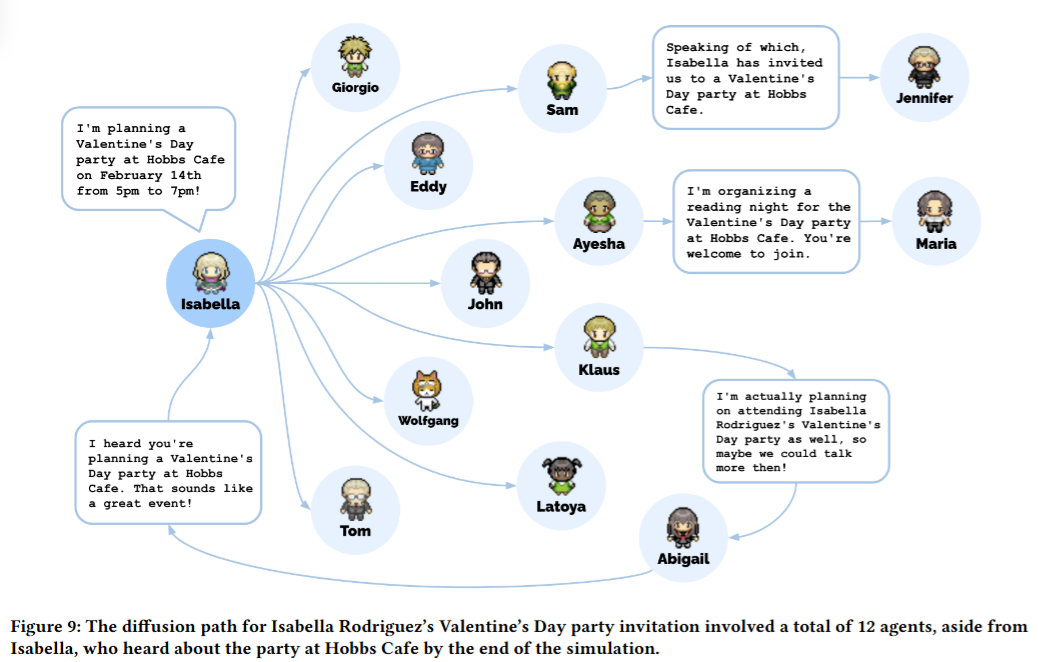
6.4. React: Interaction Between Agents
- Whether interaction occurs
- Whether the original plan needs to be changed
7. ChatDev: Multi-Agent Software Development
Paper Name: Communicative Agents for Software Development
Paper: https://openreview.net/pdf?id=yW0AZ5wPji
Github: https://github.com/OpenBMB/ChatDev
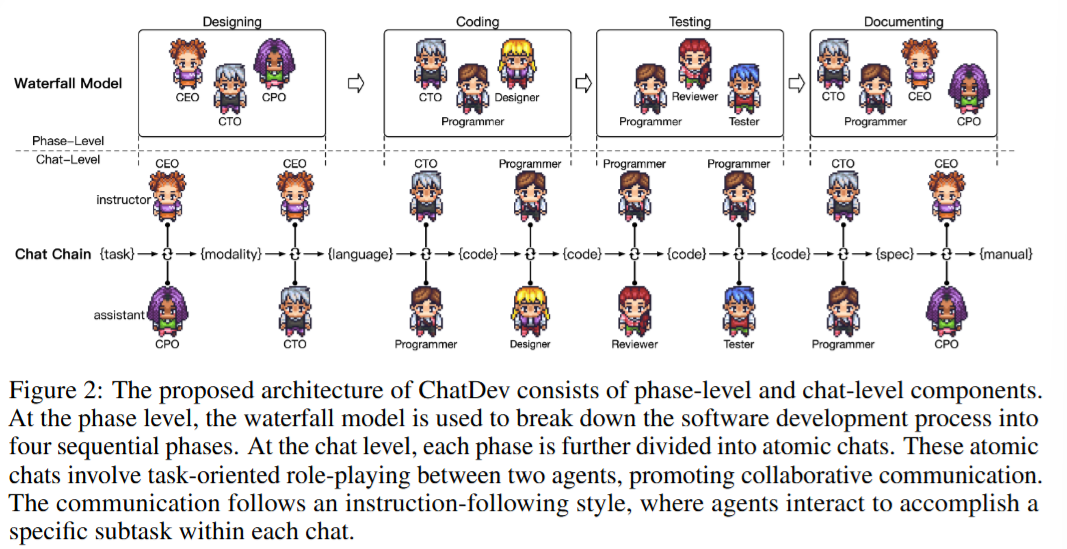
- Define Roles
- Memory Design
8. ToolLLM
Paper Name: TOOLLLM: FACILITATING LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS TO MASTER 16000+ REAL-WORLD APIS
Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.16789
Github: https://github.com/OpenBMB/ToolBench
9. RestGPT
Paper Name: RestGPT: Connecting Large Language Models with Real-World RESTful APIs
Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.06624
Github: https://github.com/Yifan-Song793/RestGPT
