Multimodal Large Models
Multimodal Large Models
- Multimodal Tasks
- Training of Multimodal Large Models
- Stable Diffusion
- LLaVA & Sora
1. Multimodal
Modality: The type of signal (or type/form of data)
- Text
- Image
- Video
- Audio
- Further subdivisions
- Graph
- Table
Multimodal: Designing with two or more different types of modalities (real-world scenarios often involve multiple signals).
Multimodal Model: An AI model capable of processing and integrating multiple modality data.
Multimodal System: A system that can handle multiple types of input and output modalities.
Multimodal Large Models (MLLMs): Large language models (LLMs) extended to handle multiple data types by incorporating additional modalities.
Multimodal large models are used to solve: Conversion between modalities
- Text → Image
- Text → Video
- Text → Table
- Text → Graph
- Image/Video → Text
2. Multimodal Tasks
The two most prominent modalities are language and vision. Related tasks can be divided into two categories: Generation and Vision-Language Understanding.
- Language Modality + Visual Modality (Text + Image)
- Generation
- Text-to-Image: Generate an image from input text
- DALL-E series
- Proposed by OpenAI
- API available
- API Documentation
- Midjourney
- Produces the best image effects
- Paid service
- Official Documentation
- Prompt Reference Library
- Stable Diffusion
- Open-source, can run on personal PCs
- Web UI: Stable Diffusion Web UI
- Model download site: Civitai, a great AI model library designed for Stable Diffusion models Civitai
- Plugin for interface localization: Chinese Interface
- Plugin - ControlNet: ControlNet Plugin
- OpenPose: Generate images based on human pose skeletons
- Canny Edge Detection: Generate images based on sketch contours
- DALL-E series
- Modify Image: Input original image and text to generate a modified image
- Text-to-Image: Generate an image from input text
- Understanding
- Visual Question Answering
- Input image and text, and answer questions based on the image-text pair
- Image Captioning
- Input image and generate a textual description of the image
- Image Classification
- For example, OCR to extract text from images or classify images
- Text-based Image Retrieval
- Method 1: Generate image descriptions, and when users input text queries, find the image description that matches the query text, then retrieve the corresponding image
- BLIP Model: Converts images into textual descriptions
- Method 2: Train a joint vector space for image and text, generate a vector for the input text, and find the image with the most similar vector
- CLIP Model: Maps images and text into a shared vector space
- Method 1: Generate image descriptions, and when users input text queries, find the image description that matches the query text, then retrieve the corresponding image
- Visual Question Answering
- Generation
- Language Modality + Auditory Modality (Text + Audio)
- Various audio-related tasks: AudioGPT GitHub
- Text-to-Speech (TTS)
- edge-tts
- edge-tts GitHub
- Uses Microsoft Edge's online text-to-speech service without needing Microsoft Edge, Windows, or API keys
- MeloTTS
- MeloTTS GitHub
- MeloTTS Hugging Face
- High-quality multilingual TTS library by MyShell.ai. Supports English, Spanish, French, Chinese, Japanese, and Korean.
- Features
- Fast, real-time speech synthesis even on CPUs
- Multilingual support
- Chinese-English mixed language support
- Easy installation
- edge-tts
- Speech-to-Text (STT), Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR)
- Voice Cloning
- GPT-SoVITS
- Music Generation
- Suno
- Suno AI: Generate full lyrics and melodies based on text prompts
- Suno
3. Stable Diffusion (SD)

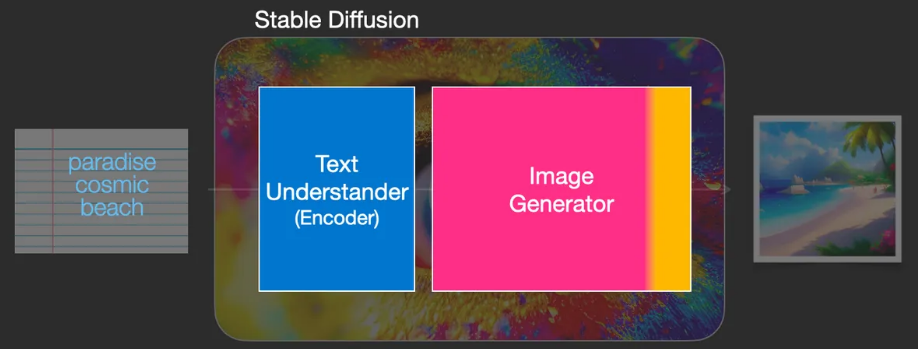
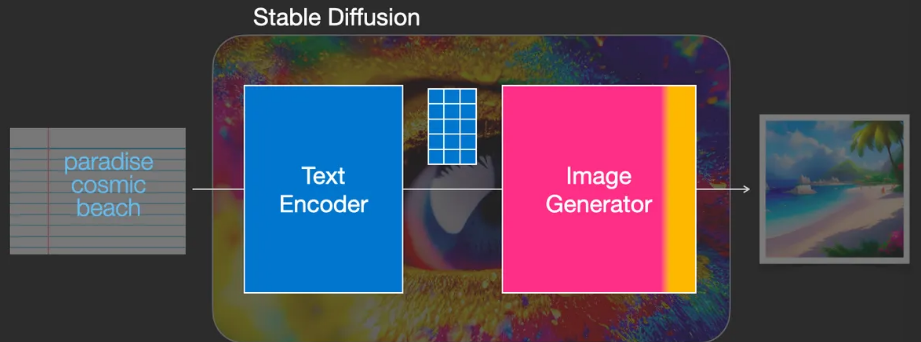
Stable Diffusion is a system composed of multiple components and models, rather than a single model.
- Text Encoder
- Vectorizes text to capture the semantic information in the text
- Image Generator
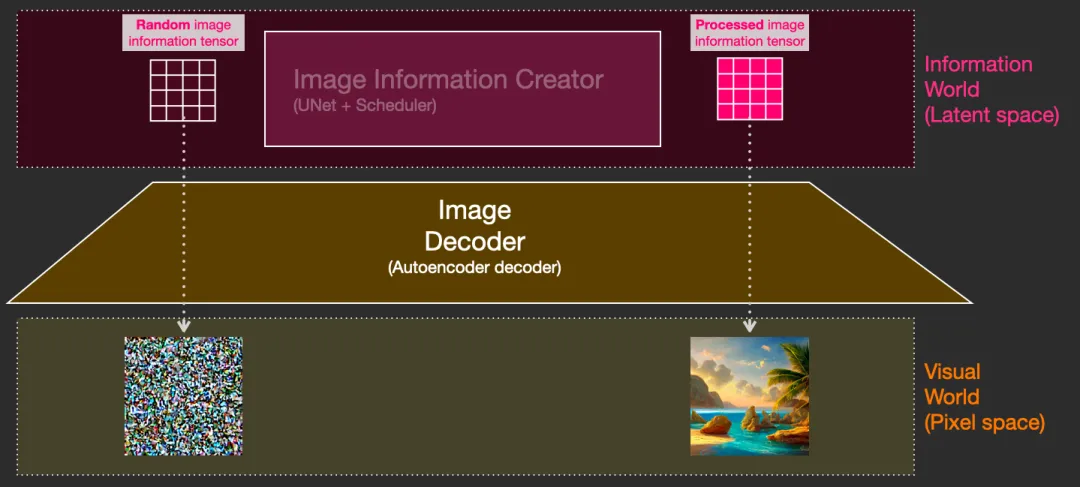
- The image generator works entirely in the latent space of image information, which makes diffusion models faster compared to earlier pixel-space diffusion models.
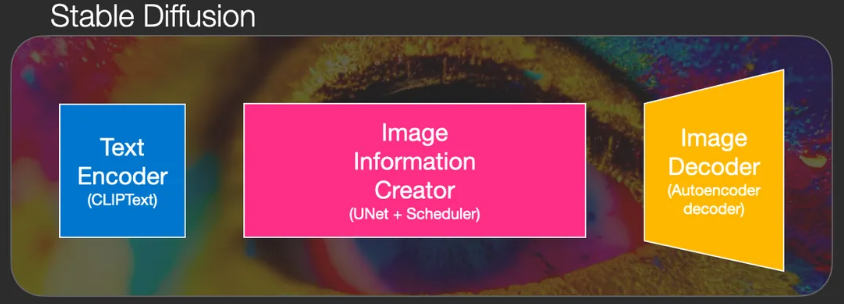
- Components
- Image Information Creator
- Image Decoder
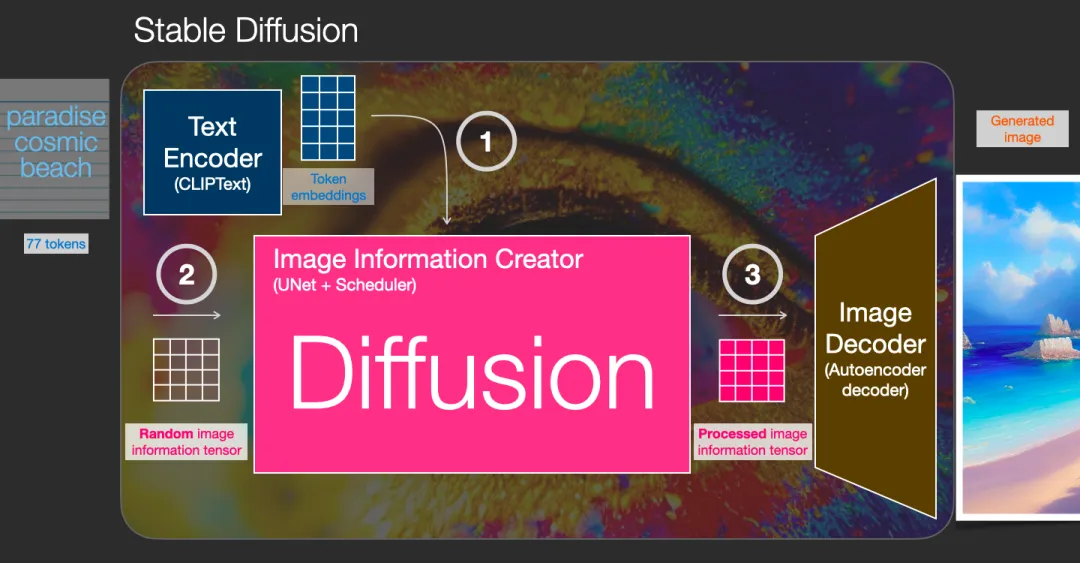
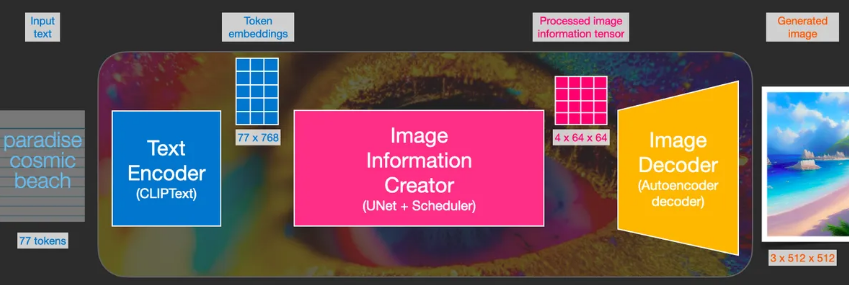
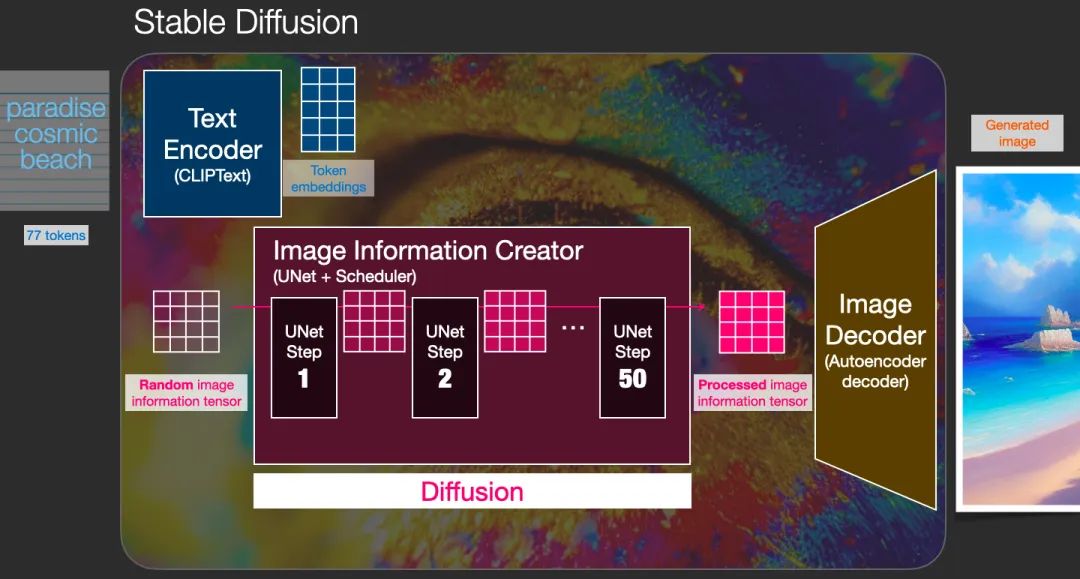
Three main components of the diffusion model (each with its own neural network):
- Clip Text (blue)
- For text encoding
- Input: Text
- Output: 77 feature vectors, each with 768 dimensions
- Grid Network + UNet + Scheduler (pink)
- Gradually diffuses information into the latent space
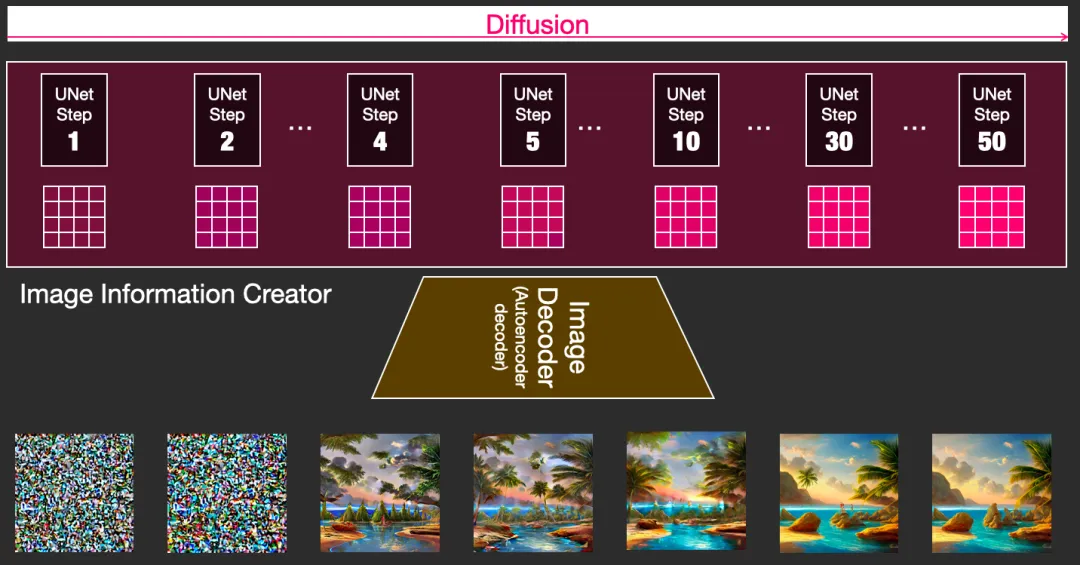
- Diffusion process: Step-by-step transformation of information, gradually adding more related information until a high-quality image is generated.
- The diffusion process contains multiple steps, each processing the latent matrix and generating a new latent matrix to better match the "input text" and "visual information" from the model's image bank.
- Input: Text vector and random initial image information matrix (latent)
- Output: Processed information array (dimension: (4, 64, 64))
- Autoencoder Decoder (orange)
- Draws the final image
- Input: Processed information array
- Output: Resulting image (dimension: (3, 512, 512))
Diffusion model working principle:
- Forward Diffusion
- Adds noise to training images, gradually turning them into noise images without distinct features.
- Reverse Diffusion
- Starts with noisy, meaningless images and gradually restores images of cats or dogs by reversing the diffusion process.

4. Training of Multimodal Large Models
- Traditional Training Methods
- End-to-End Training
- Image Captioning Task: Image → Description/Caption
- Image → CNN → Vector (shared) → RNN/LSTM → Text (Encoder-Decoder structure)
- Training Data: (Image1, Des1), (Image2, Des2), ..., (ImageN, DesN)
- Problems
- Training from scratch is costly
- Each task requires large datasets, and manually annotating data is difficult without large models
- End-to-End Training
- Training Multimodal Large Models
- Foundation Models
- Text Domain
- GPT-4, LLaMA, ChatGLM, Qwen
- Image Domain
- CLIP
- Video Domain
- Sora
- Graph Domain
- GNN
- Text Domain
- Multimodal Systems
- Text (language models) as the intermediary (since all other modalities reduce to expressing meaning)
- Image/Video/Graph → Each modality has its adapter → Align Language model, Image model, Video model, and Graph model (making modalities aligned)
- Advantages
- Lower training costs
- Only the adapters for each modality are trained, while the foundation model parameters remain frozen
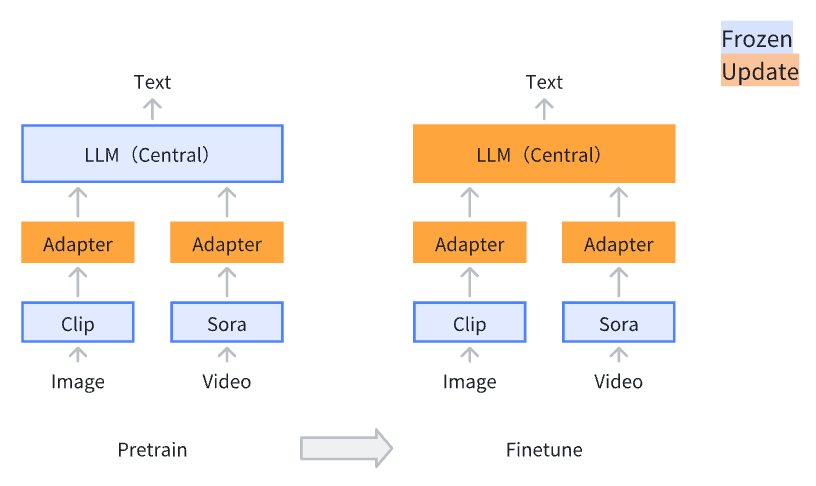
- Stage 1: Pre-training for Feature Alignment
- Only the adapter parts are updated
- This step is necessary because the adapters are newly introduced and initially have no effect
- Large amounts of data are required for this stage
- Stage 2: Fine-tuning End-to-End
- Both the adapter and the language model parts are updated
- This stage requires a smaller amount of data
- Stage 1: Pre-training for Feature Alignment
- Only the adapters for each modality are trained, while the foundation model parameters remain frozen
- Easier adaptation for each task
- Lower training costs
- Foundation Models
5. Flamingo
Github: https://github.com/lucidrains/flamingo-pytorch
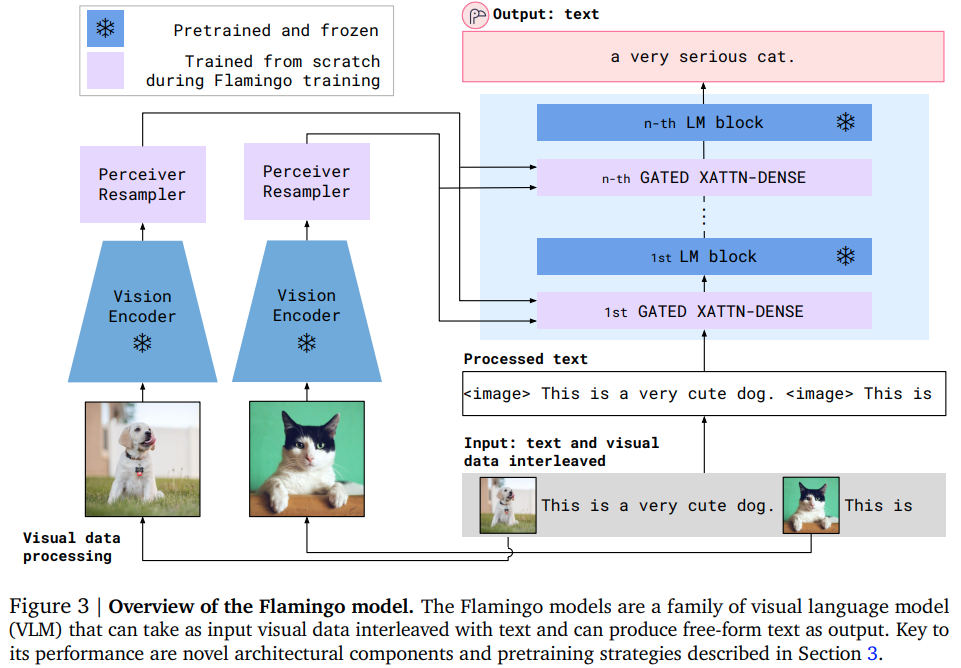
- Input: image + text + image + text (Images and text alternate)
- Vision Encoder: Base model for processing images - Foundation Models
- Perceiver Resampler: Adapter
- LM block: Language Model
6. LLaVA
Github: https://github.com/haotian-liu/LLaVA
Paper Name: Visual Instruction Tuning Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.08485
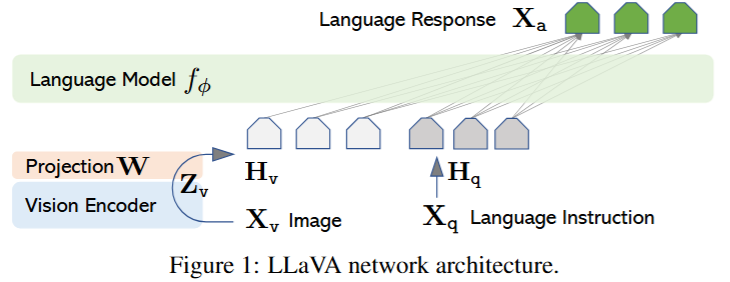
- Vision Encoder: Base model for processing images - Clip
- provides the visual feature
- Projection W: Adapter, converts to a vector with the same dimension as text
- apply a trainable projection matrix W to convert into language embedding tokens H
- Language Model: Vicuna
Only the adapters for each modality need to be trained, while the parameters of the base models for each modality remain frozen.
- Stage 1: Pre-training for Feature Alignment
- Only the adapter parts are updated
- Stage 2: Fine-tuning End-to-End
- Both the adapter parts and the language model parts are updated
Data Generation: GPT-assisted Visual Instruction Data Generation
- The prompts provided to GPT include text descriptions (Captions) and bounding boxes, but do not include the images themselves. The GPT used is also a pure language model.
- Text Description Caption
- Bounding Box
- GPT's responses include
- Q&A pairs (QA Conversation)
- Detailed Description
- Complex Reasoning

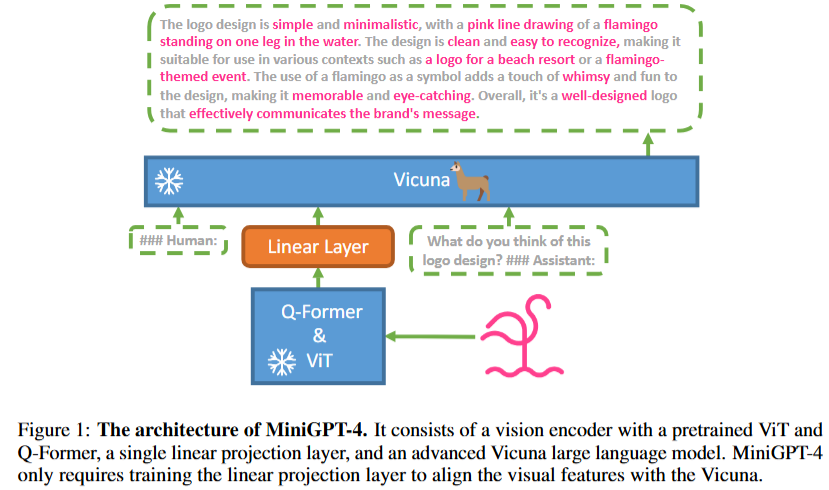
7. MiniGPT-4
Github: https://github.com/Vision-CAIR/MiniGPT-4
Paper Name: MINIGPT-4: ENHANCING VISION-LANGUAGE UNDERSTANDING WITH ADVANCED LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS
Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.10592
8. Sora Video Generation Large Model
Paper Name: Sora: A Review on Background, Technology, Limitations, and Opportunities of Large Vision Models
Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2402.17177
Github: https://github.com/lichao-sun/SoraReview
Note: This is not an official technical report from OpenAI.
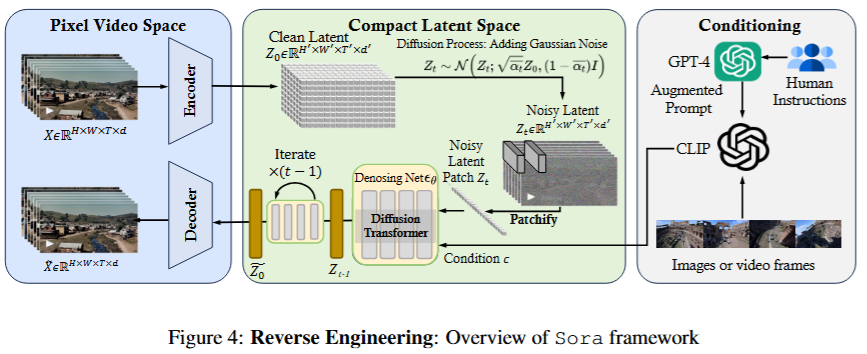
Sora is essentially a diffusion transformer model with flexible sampling dimensions. It consists of three parts:
- Time-Space Compressor: Maps the original video into latent space
- A time-space compressor: maps the original video into latent space.
- Vision Transformer (ViT): Processes the tokenized latent representation and outputs the denoised latent representation
- A ViT then processes the tokenized latent representation and outputs the denoised latent representation.
- CLIP-like Model: Guides the video generation process, creating videos with specific styles or themes
- A CLIP-like conditioning mechanism receives LLM-augmented user instructions and potentially visual prompts to guide the diffusion model to generate styled or themed videos.
9. Prospects of Multimodal Large Models
Current Status
- In the early stages
- Rapid technological iteration
- In the long run, it is the endpoint of large models
Analysis of Development in the Field of Large Models
- The foundation of multimodal large models is text large models
- The upper limit of text large models determines the upper limit of other large models
- Text large models will promote the development of other modalities
- Other modalities will subsequently develop the text large models
Opportunities in 2024
- Agent
- Small Model/Model Quantization/Fine-tuning Small Models (Models embedded in smart devices, 0.5B, 1B)
- Smart hardware, such as smartwatches
- How to run models on CPUs
- Multimodal
- Inference acceleration, reducing inference costs
